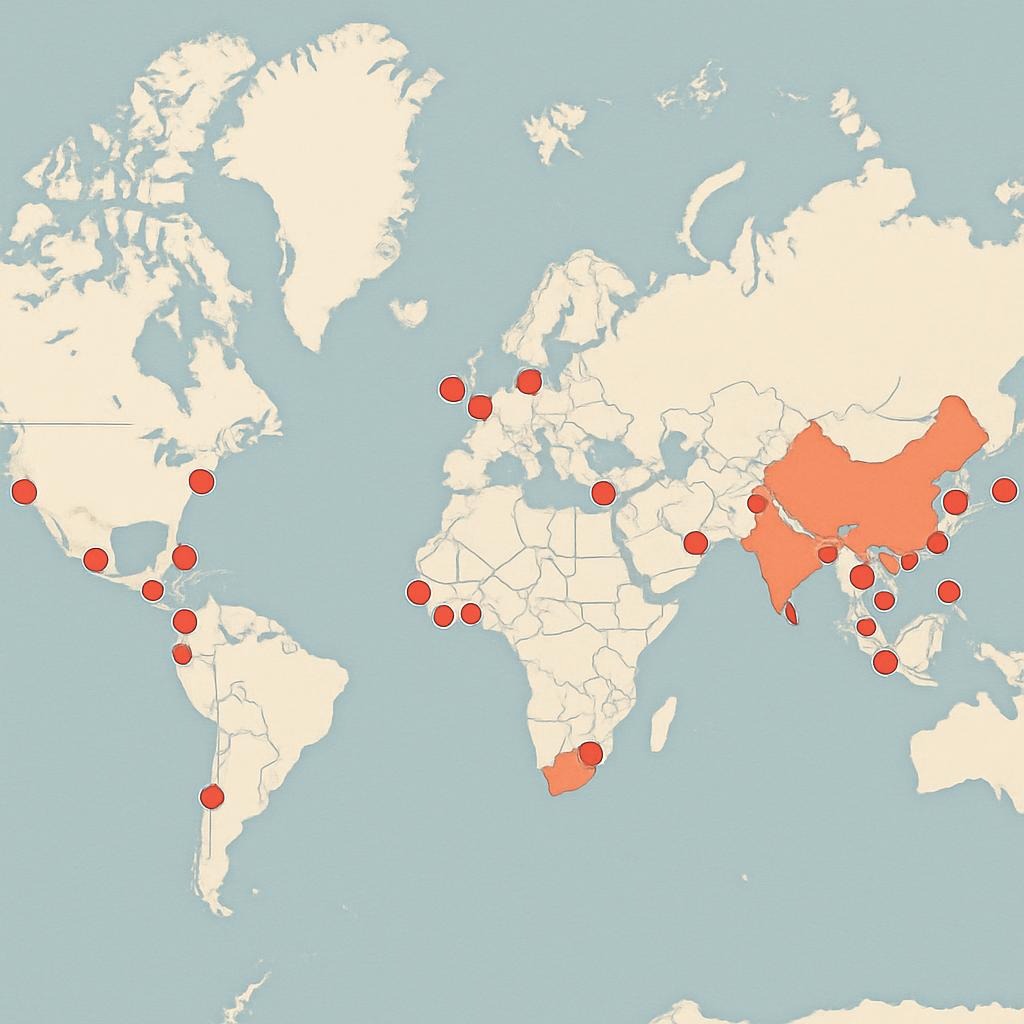
China currently operates or owns stakes in 129 overseas ports across every major region, including Europe, Africa, Latin America, South Asia, and the Arctic economy.ac. This vast network is a direct extension of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which has enabled China to finance, build, and control strategic maritime infrastructure under the guise of development cooperation niice.org.np.
Key Insights by Region and Sector
🧭 Strategic Port Control
- Global Port Reach: Chinese firms control or operate 129 overseas ports, with major concentrations in Europe (30+ ports), Africa (78 ports), Latin America (31 ports), and South Asia economy.ac Africa Center for Strategic Studies chinastrategy.org.
- BRI’s Maritime Role: The BRI’s Maritime Silk Road facilitates China’s port acquisitions, enabling dual-use infrastructure and strategic access to global trade routes niice.org.np Wikipedia.
- Port of Piraeus, Greece: COSCO’s 67% stake transformed Piraeus into Europe’s fastest-growing port, shifting trade flows toward Chinese-controlled logistics hubs GreekReporter.com China-CEE Institute.
- Djibouti & Mombasa: These ports serve as logistical nodes for Chinese naval access, raising concerns about sovereignty and military dual-use capabilities Africa Center for Strategic Studies eurafrica.info.
- Latin America: China’s control of ports like Chancay in Peru challenges U.S. influence, offering Beijing strategic proximity to the Panama Canal and regional supply chains features.csis.org Council on Foreign Relations.
- Gwadar, Pakistan: Gwadar offers China a direct link to the Arabian Sea, bypassing the Strait of Hormuz and enhancing energy security and naval reach Springer Middle East Institute.
- Indian Ocean Strategy: Ports in Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Pakistan form the backbone of China’s “String of Pearls” strategy, encircling India and securing maritime chokepoints Wikipedia swadeshishodh.org.
- Arctic Concerns: Investments in Russia and Greenland raise alarms over resource control and geopolitical leverage, though many deals have stalled or been scaled back The Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs POLITICO.
- Military Logistics: Chinese port acquisitions often include dual-use infrastructure, enabling potential military deployment under civilian cover 日本国際問題研究所 Newsweek.
- Cyber Risks: Chinese-made cranes and software in U.S. ports pose data surveillance and cyber exploitation threats, prompting federal scrutiny CNBC Maritime Administration.
🌐 Global Corporate Influence
- Major Holdings: Chinese firms hold stakes in Syngenta, Riot Games, TikTok (ByteDance), and multiple European tech startups, influencing agriculture, entertainment, and AI IMD Business School moneydigest.com The Diplomat.
- Syngenta’s Impact: ChemChina’s $43B acquisition of Syngenta reshaped global agrochemical supply chains, raising concerns over food security and IP transfer IMD Business School The Case Centre.
- European Tech: Chinese investment in AI and semiconductors has led to IP leakage and innovation dependency, prompting EU regulatory pushback Mercator Institute for China Studies (MERICS) Rhodium Group.
- Conglomerate Reach: COSCO, China Merchants, and CITIC operate across shipping, finance, manufacturing, and infrastructure, often in strategic alignment with state goals 中远海运 POLITICO.
- Energy Markets: State-owned enterprises like China Three Gorges and Sinopec dominate energy infrastructure in Latin America and Africa, influencing grid access and pricing IEA – International Energy Agency CSIS.
- Rare Earths: China controls 70% of mining and 90% of processing, affecting global tech manufacturing and prompting Western efforts to diversify supply chains DW SFA (Oxford).
- Media & Gaming: Tencent owns Riot Games and stakes in Epic Games, while ByteDance’s TikTok shapes global content consumption, raising soft power concerns PCGamer The Diplomat.
- Silicon Valley: Chinese VC firms have invested in AI, robotics, and biotech startups, sparking U.S. national security reviews and tech transfer fears Federal Reserve Board archivemacropolo.org.
- Logistics Acquisitions: Chinese firms have acquired European and African logistics companies, integrating supply chains under Chinese control Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business wcl.de.
- Regulatory Navigation: Chinese companies increasingly face national security reviews in the U.S., EU, and India, with growing scrutiny of data, IP, and strategic sectors International Bar Association HG.org Lawyers Directory.
🧩 Geopolitical and Economic Implications
- Sovereignty Risks: Long-term leases, equity stakes, and debt-for-assets swaps (e.g., Hambantota) have compromised host nation autonomy CSIS War on the Rocks.
- Economic Dependencies: Infrastructure loans often lead to debt traps, limiting fiscal flexibility and increasing reliance on Chinese capital Democracy in Africa The Geopolitics.
- IMF & World Bank Response: Multilateral institutions are recalibrating strategies to compete with China’s lending, emphasizing transparency and sustainability CEPR IMF eLibrary.
- Countermeasures: India, Japan, and the U.S. are investing in alternative infrastructure, tech alliances, and Indo-Pacific security frameworks to counterbalance China The Diplomat Foreign Policy Research Institute.
- Xi Jinping’s Strategic Vision: China’s global investments align with Xi’s goals of economic resilience, technological dominance, and geopolitical leverage, as outlined in the Dual Circulation strategy and Five-Year Plans Mercator Institute for China Studies (MERICS) beijingpost.com.
🎥 Recommended Documentaries
| Title | Focus | Link |
|---|---|---|
| China’s New Silk Road (DW) | BRI and global infrastructure | Watch here |
| The China Hustle | Corporate influence and financial risks | Watch here |
| Frontline: China’s COVID Secrets | Governance and global strategy | Watch here |
| Inside China’s Tech Rise (BBC) | AI, surveillance, and global tech | Watch here |
| China’s Arctic Ambitions (CBC) | Arctic geopolitics and resource control | Watch here |
🔑 Keywords
China, Belt and Road Initiative, strategic ports, COSCO, Gwadar, Piraeus, dual-use infrastructure, rare earths, Syngenta, Silicon Valley, cyber surveillance, sovereignty, debt trap, Xi Jinping, global supply chains, Arctic investments, String of Pearls, energy markets, media influence, logistics acquisitions, national security reviews





